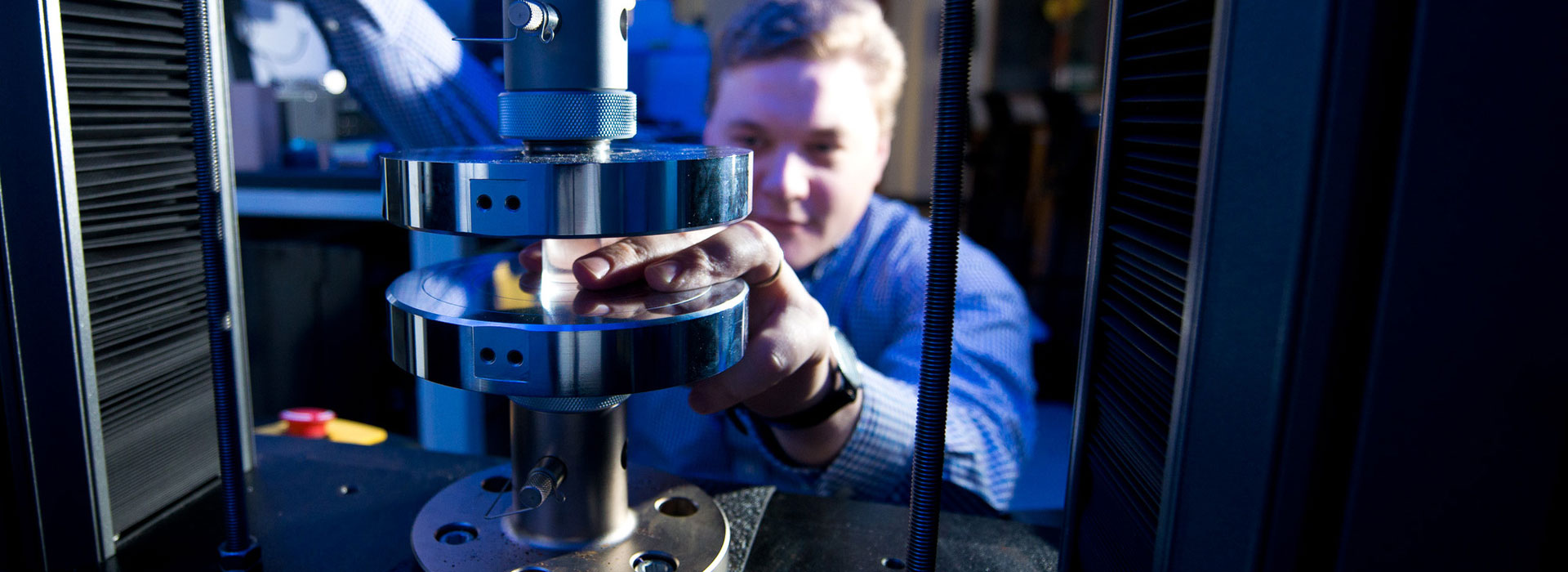


EUROLAB, with its state-of-the-art accredited laboratories and expert team, provides precise and fast testing services within the scope of ASTM D4253 testing. This standard covers the determination of the unit weight of the maximum index dry density of cohesionless, free-draining soils using a vertically vibrating table.
To be consistent with the applicable definition given in Chapter 3 on terminology, "pre-dry density or unit weight is not used in the title and remainder of this standard. The test apparatus described in this standard was developed and manufactured using values in the gravimetric or inch-pound system. Therefore, inches Tester dimensions and mass given in -pound units are considered standard.
It is common practice in the engineering profession to use pounds to represent both units of mass (lbm) and units of force (lbf). This indirectly combines two separate unit systems; that is, the absolute system and the gravitational system. It is scientifically undesirable to combine the use of two separate inch-pound units into a single standard. This standard was written using the system of gravity units when dealing with the inch-pound system. In this system, the pound (lbf) represents a unit of force (weight). However, scales or scales measure mass; and weight must be calculated. In the inch-pound system, it's common to assume 1 lbf equals 1 lbm. While reporting density is not considered a non-compliance with this standard, unit weights should be calculated and reported as the results can be used to determine force or stress.
The terms density and unit weight are often used interchangeably. Density is mass per unit volume while unit weight is force per unit volume. In this standard, density is given in SI units only. Once density is determined, unit weight is calculated in SI or inch-pound units, or both.
Alternative method is provided to determine the maximum index density/unit weight as follows:
When starting a new job or encountering a change in soil types, it is recommended to apply both dry and wet methods, as the wet method can yield significantly higher maximum index values. Density/unit weight for some soils. Such a higher maximum index density, together with the minimum index density unit weight, will appear to significantly affect the value of the relative density of Test Methods D4254. Calculated for a soil encountered in the field. While the dry method is often preferred as results can often be obtained faster, as a general rule the wet method should be used if it is determined that it produces maximum index densities/unit weights that will significantly affect the use/application of the value.
These test methods are applicable to soils that may contain up to 15% dry mass, soil particles passing through a No. 200 (75-μm) sieve, provided they still have cohesion-free, free-draining properties. In addition, these test methods are applicable to soils where 100% of soil particles by dry mass exceed 3 inches. (75 mm) sieve.
For the purposes of these test methods, soils shall be regarded as naturally occurring non-cohesive soils, treated particles or composites or mixtures of natural soils, or mixtures of natural and treated particles, provided they are free-draining.
These test methods will typically produce a higher maximum dry density unit weight for cohesionless, free-draining soils than is achieved with impact compaction where a well-defined moisture-density relationship is not apparent. However, for some soils containing 5% to 15% fines, the use of impact compaction can be useful in assessing what an appropriate maximum index density/unit weight is.
EUROLAB assists manufacturers with ASTM D4253 test compliance. Our test experts, with their professional working mission and principles, provide you, our manufacturers and suppliers, the best service and controlled testing process in our laboratories. Thanks to these services, businesses receive more effective, high-performance and quality testing services and provide safe, fast and uninterrupted service to their customers.
To get an appointment, to get more detailed information or to request an evaluation, you can ask us to fill in our form and reach you.