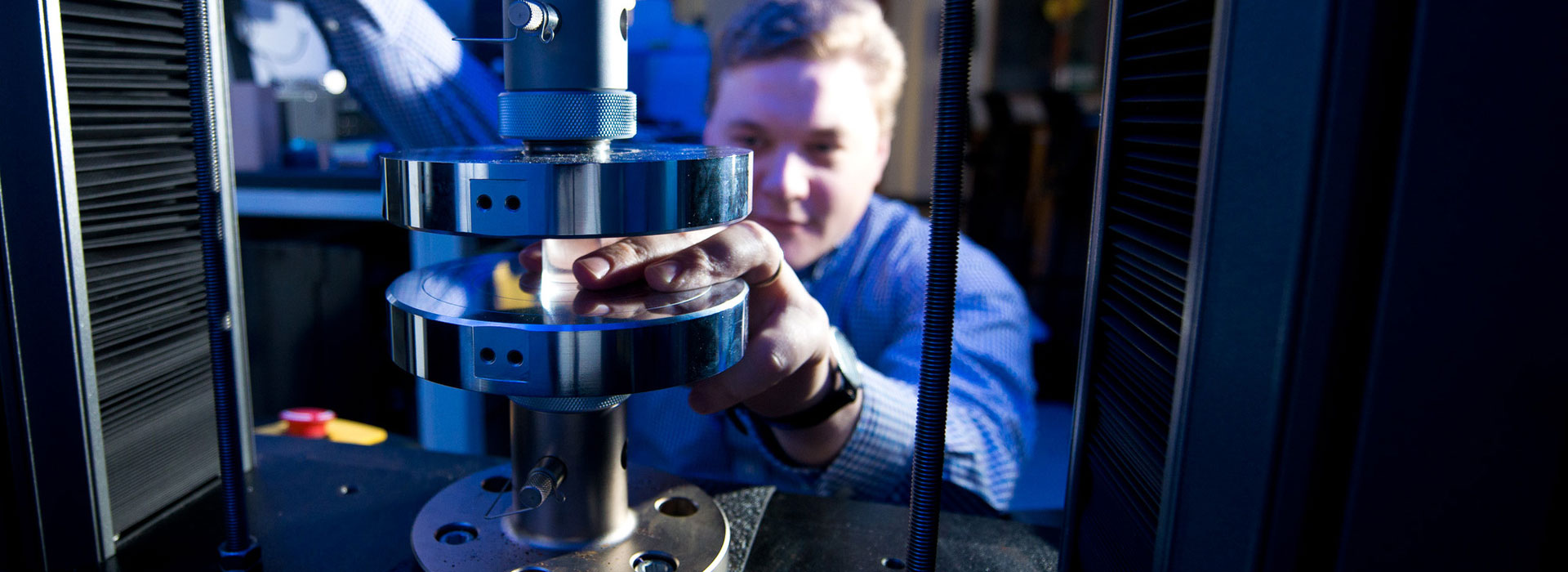


The ASTM F897 test provides a screening test to determine the amount of metal loss from plates and screws used for osteosynthesis (internal fixation of broken bones) due to worry corrosion in the contact area between the screw head and the plate hole opposing region.
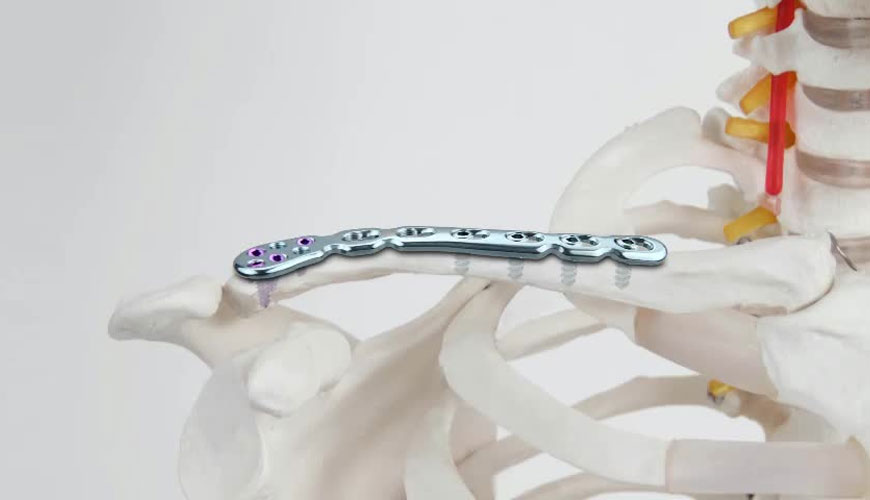
It is well known from examination of implants after use that plates and screws used for osteosynthesis are subject to metal loss due to corrosion at plate-screw interfaces. One of the mechanisms of this abrasive attack is to cause corrosion due to relative motion (micromotion) between screw heads and plate hole counter holes.
It is also known that the release of corrosion products into the tissues surrounding the implant may have adverse effects on the local tissue or have systemic effects. Therefore, it is important to minimize the amount of tissue exposure to corrosion products.
Implants are used in the form in which they will be used clinically. The described machine creates a relative motion between plates and screws that simulates a type of motion pattern that can occur when these devices are used clinically.
Because the environmental and stress conditions used in this test method may not be the same as those experienced by bone plates in the human body, this test method can produce alarming corrosion rates that are lower or higher than those experienced in practice. The proposed 400 N axial load was chosen in a range where the amount of corrosion of concern is not sensitive to small changes in axial load. The recommended combination of load and angular displacement is that measurable wear of surgical alloys occurs in a relatively short period of time (7 to 14 days).
The device is designed to facilitate sterilization of test specimens and test chambers to allow testing with proteinaceous solutions that would be contaminated by microbial growth in non-sterile conditions. The samples used may be standard osteostyrenesis implants or materials manufactured in appropriate shapes.
This test method can be used to test fretting corrosion of metal plates and screws of similar or different alloy composition, or to test for fretting corrosion of metal-nonmetal combinations. This test method can also be used for wear or deterioration studies of nonmetallic materials. This test method can be used as a screening test to rank corrosion of saline or proteinaceous solutions, or to rank metal-to-metal pairs for resistance to corrosion, or to examine other material combinations.
Values stated in SI units or inch-pound units should be considered separately as standard. The values specified in each system may not be exactly equivalent; therefore, each system will be used independently of the other system. Combining values from the two systems may result in non-compliance with the standard.
This standard may contain hazardous materials, operations and equipment. This standard is not meant to address all safety concerns associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to consult and establish appropriate safety and health practices and to determine the applicability of regulatory restrictions prior to use.
Our organization also provides testing services within the scope of ASTM F897 Standard Test Method for Measuring Fretting Corrosion of Osteosynthesis Plates and Screws, within the framework of laboratory testing services.
To get an appointment, to get more detailed information or to request an evaluation, you can ask us to fill in our form and reach you.