
Ion chromatography testing provides cleaning information, especially individual ionic data values, for various sample types, including, but not limited to, printed circuit boards, printed circuit assemblies, and soldering flows.

The use of Ion Chromatography (IC) in the printed circuit board / assembly industry has increased significantly over the past decade. As the cabinet / assembly circuit decreases in "size", the cleaning of said boards / assemblies has become increasingly important, and the IC offers a lot of useful information in this area. Also, the end use of the product - the consumer, military, aviation and telecommunications, and medical - can also affect the “needed” cleanliness due to the required level of reliability.
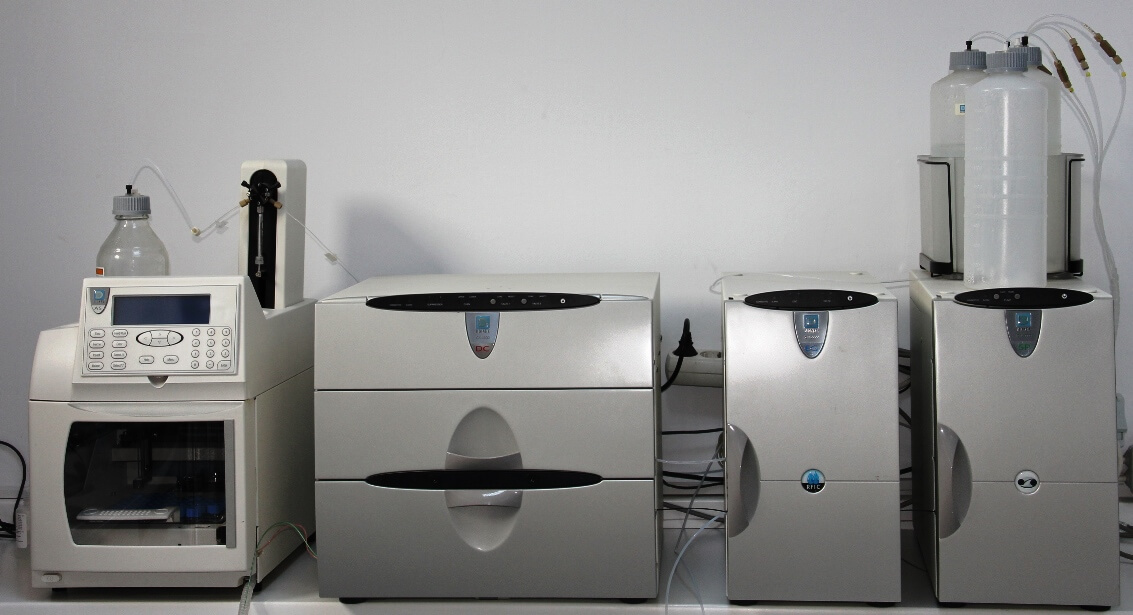
Ion Chromatography provides individual data values for the specific ionic species selected for the test. This is much more effective than in the past, as opposed to the "traditional" cleaning test, where only one "clean" measure was provided. In general, to better fit the industry as a whole, the Ion Chromatography test is used not only with printed circuit boards and assemblies, but also solder fluxes, unit enclosures, electrical components, surface mount adhesives, etc. Also adapted for other related products such as.
Ion Chromatography allows to obtain many unique data in providing accurate qualitative and quantitative determinations related to the material identification of anions and cations. Targeted analytes refer to positively and negatively charged ions that often occur in processes where electrons are transferred between metal and non-metal materials. The ability to isolate and detect trace ionic species, weak organic acids, silicates, carbohydrates, amino acids and other substances makes IC effective in a wide variety of test programs.
From trace analysis to discover contamination in soil and water samples and drinking water, it is among the common applications from the analysis of electrolyte and owner properties in electroplating bath processes. Ion Chromatography can also identify total halides from pyrohydrolysis extraction and allow purification of complex multimeric protein assemblies.
Ion Chromatography is an advanced testing program that is highly selective and can analyze molecular species rather than focusing on existing elements. It is used by a wide range of industries due to its broad analytical properties. From clinical benefits to industrial applications, ion chromatography is effective in ensuring the separation of almost all types of ions and molecules.
Ion Chromatography is widely used in determining environmental elements such as soil and water, as well as purity of consumables. It can also help measure the quality of molecular materials and minerals accurately. It is used in a variety of industries, from healthcare, life sciences and drug production to local and official environmental testing, commercial food and beverage packaging and production, protein purification, energy production and quality control.
When evaluating samples by ion chromatography, the following specified test methods are widely and frequently used by the industry:
In addition to these established methods in which all samples or materials are analyzed, the Ion Chromatography test is also widely used to investigate "local" interests in a sample. When residual or foreign matter is observed in a printed circuit board or assembly, "localized" extraction techniques can be used to obtain samples that can then be analyzed by IC.
For process control or characterization, replicate samples taken from various steps in the assembly process are frequently analyzed to determine “baseline” values. While these "core" values can then be used to evaluate process variation and control, when combined with reliability testing, they can also be used to potentially determine cleaning limits or requirements for future tests.
For failure analysis, Ion Chromatography testing can be performed when the failure mode of a product is potentially related to the unwanted presence of ionic material. Typically, this ionic material will cause some kind of high resistance among the areas that need to be electrically isolated. The test itself can be done on bare printed circuit boards, fully filled printed circuit groups, or anywhere between them. In addition, both "full" and "localized" extraction techniques can be used. Ultimately, the ionic information obtained can be used in conjunction with other failure analysis techniques to isolate and identify the potential root cause of the problem at hand.
As EUROLAB, we are among the most innovative and reliable providers of Ion Chromatography Test and certification services for product developers, manufacturers and environmental organizations. For more information on Ion Chromatography Test programs, contact us and request a free quote today.
To get an appointment, to get more detailed information or to request an evaluation, you can ask us to fill in our form and reach you.