
The Armed Services Committee (SASC) reported that 1.800 suspected counterfeit ingredient cases have entered more than 1 million individual products. SASC announced these findings during the Defense Ministry Supply Chain Counterfeit Electronic Parts trial held on November 17, 2011.

If you consider this number for the army, the number of imitations in our commercial but high-reliability products, just like life support or other critical systems, may be much higher than our estimates.
Components that are scrapped, components in recycled products, or cheap components can be "re-specified" and sold as a new, more expensive, more reliable version. Among the reasons for the spread of counterfeiting are profitability, the export of electronic waste for disposal in poorer and less likely countries.
Most of the efforts made today are not to prevent fraud, but rather to screen components for identification and removal of counterfeit products before being used in a finished product.
Succeeding in the fraud war cannot be guaranteed by specifying a list of several screening tests in the purchase document, which only allows the counterfeiter to determine how to avoid detection. Efforts to detect and prevent counterfeiting of electronic components should show creativity and determination of counterfeiters.
If you determine that you need to act, EUROLAB staff can help you create the plan that is right for you, and the first consultation is free. The program can be as simple or complex as you want.
In general, used components are renewed and re-sold or re-labeled and sold as something different. Scanning techniques detect specific marks from each of these processes.
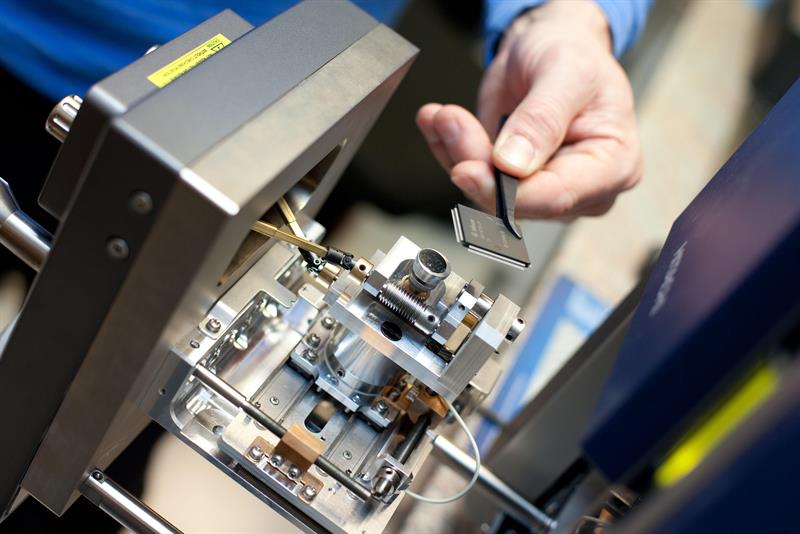
Visual Inspection is the simplest and fastest of inspection techniques that require only an optical microscope, a few chemicals, and a trained eye - the most important of all three. An experienced inspector can identify sanding marks, blackout proofs, rework proofs, twisted cables, repeated cables, the definition and quality of markings, appropriate marking and logos, and replacement of initial features on a component.
Electrical inspection can range from a few electrical measurements to complex measurements at varying temperatures using automated equipment and special software.
An x-ray examination of an electronic component, such as an x-ray of a broken bone, provides the simplest image to internal structures. X-ray examination becomes even more effective when questionable components can be compared to a known original part.
Decapsulation involves destroying part sampling. Decapsulation can be performed mechanically or chemically by removing the cap or top layers of the component body to reveal the mold and the internal structures of the component.
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) is of great benefit in the examination of the microscopic internal structures of the components. Like the X-Ray, SEM examination also benefits by directly comparing it with an known authentic episode.
Combined with Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDS), the microscopic areas of the component can be compared for element components.
X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF), such as EDS, is used to identify essential components.
Counterfeit products continue to improve their craft; they also know the traditional techniques used to describe their products and change their processes so that traditional fixing techniques are not effective.
Some of these techniques, like FTIR, are newly used in the authenticity test; others are older techniques used by new methods, such an x-ray machine has been calibrated specifically for counterfeit examination.
These tests are done in a similar way to traditional techniques, but without the restrictions of industry standard test methods, chemical solutions and static procedures used for decades.
SEM is more commonly used as a technique to detect subtle differences of blackout. EDS is used to detect minor fundamental differences between dimming and the actual component body.
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) is a method used to identify organic compounds. The polymers that contain the blackout material used to hide the component body and evidence of forgery are all organic materials.
Ion Chromatography (IC) is another technique that can be used to detect a third form of contamination - ionic. Ionic contamination is usually found in the form of salts or organic acids and can accumulate on a piece through the use or application of chemicals during the counterfeiting process.
Scanning Acoustic Microscopy (SAM), an ultrasound form, has been shown to be an effective screening tool against counterfeiting. SAM uses cyclic sound waves to determine density differences within a sample.
There are several thermal analysis techniques that can be used in a small sampling of the component body. Thermal analysis measures some chemical or mechanical properties as a function of temperature.
Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), a technique, measures chemical reactions as a function of temperature. Another technique, Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA), measures weight loss as a function of temperature.
Finally, Thermomechanical Analysis (TMA) measures dimensional change as a function of temperature. Two important properties that can be examined are the softening point and thermal expansion coefficient (CTE) of a polymer.
To get an appointment, to get more detailed information or to request an evaluation, you can ask us to fill in our form and reach you.