
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMI) flexibility is a crucial requirement for power-related applications such as electric vehicle charging, whether the electric charging station is in a public space with multiple ports or a single stand-alone unit typically used in residential settings.

Electric vehicle supply equipment, commonly referred to as charging stations, has three to four major subsystems, each requiring electromagnetic compatibility protection from other subsystems, depending on the type of equipment. Filtering, shielding, and improved printed circuit board (PCB) layout are ways to reduce electromagnetic compatibility, but these techniques are costly.
In general, AC chargers have subsystems for AC-DC conversion, human-machine interface, and system monitoring at a minimum. DC chargers have an additional subsystem for DC-DC conversion. Battery buffer charging stations, on the other hand, allow batteries in electric vehicle supply equipment to be charged during off-peak hours, helping offset the high recurring cost of using electricity during peak hours. Rather than using a DC-DC subsystem, such chargers require a battery management system to monitor the health of the batteries.
The biggest concern for electric vehicle owners is knowing when and how to charge their vehicles. Because unlike fuel vehicles, charging an electric vehicle requires a little more planning, but with increasing demand and incentives for alternatives to gas-powered cars, electric vehicle charging stations are becoming increasingly common.
All electric vehicles, like any rechargeable device or electronic device, need an electric vehicle (EV) charger to keep the battery charged. Essentially, an EV charger draws an electrical current from a 240v outlet or the mains it is connected to and delivers that electricity to the vehicle, just like any other device that is charged by plugging it into the wall.
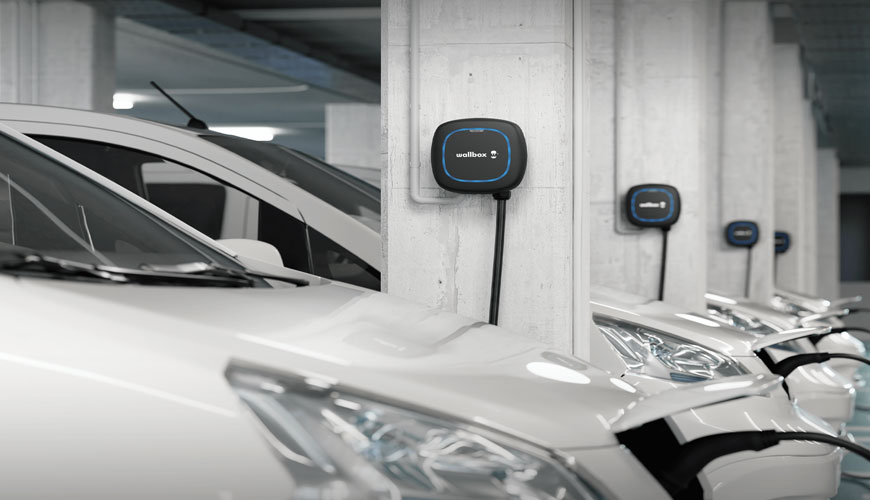
A charging station, also known as a charging point or electric vehicle supply equipment, is a power supply device that provides electrical power to charge any plug-in electric vehicle, including battery electric vehicles, electric trucks, electric buses, and rechargeable hybrid vehicles.
There are essentially two basic types of electric vehicle chargers: alternating current (AC) charging stations and direct current (DC) charging stations. Electric vehicle batteries can only be charged with direct current electricity, whereas most mains electricity is supplied as alternating current from the electrical grid. That's why most electric vehicles have an AC-DC converter, commonly known as an onboard charger. In an AC charging station, AC power from the grid is converted into DC power to recharge the battery in this charger. DC chargers, on the other hand, place the converter in the charging station rather than in the vehicle to avoid size and weight restrictions, facilitating higher-power charging. Most new electric vehicles accept both AC and DC power.
Just like other electrical equipment, electric vehicles and charging cables need to be inspected and tested regularly to ensure they are in a safe condition. These tests are often required for insurance reasons, and many commercial and industrial facilities require proof of this testing before equipment can be put into use. Regular testing can also reveal any necessary preventative maintenance before it becomes a problem.
Likewise, charging cables should be visually inspected before each use. Wiring separate from the vehicle should also be electrically tested annually. This is the longest period a cable should be used between tests and assumes a professionally installed cable is used in a fixed location that is not subject to heavy use and is protected from physical damage, water ingress, and other factors such as extreme weather conditions.
Any socket to be used for electric vehicle charging should be electrically checked before first use and at regular intervals thereafter, at least once a year. Some sockets in electrical installations should not be used to charge electric vehicles.
Among the numerous testing, measurement, analysis and evaluation studies it provides for businesses in various sectors, our organization also provides electric vehicle charging station testing services with its trained and expert staff and advanced technological equipment.
To get an appointment, to get more detailed information or to request an evaluation, you can ask us to fill in our form and reach you.