

The ISO 8692 standard, developed by the International Standards Organization (ISO), specifies a method for determining the growth inhibition of unicellular green algae by substances and mixtures found in water or wastewater. This method is applicable for substances that dissolve easily in water.
With modifications to this method as specified in ISO 14442 and ISO 5667-16, the inhibitory effects of poorly soluble organic and inorganic materials, volatile compounds, heavy metals and wastewater can be tested. A rapid algae growth inhibition screening test for wastewater is described in an appendix.
An alternative test procedure with algae from algae beads by direct measurement of algae growth in spectrophotometric cells is described in an appendix.
Persons using this International Standard should be familiar with normal laboratory practice. This International Standard does not purport to address all, if any, safety problems associated with its use. It is the user's responsibility to establish appropriate safety and health practices and to ensure compliance with any national regulatory requirements.
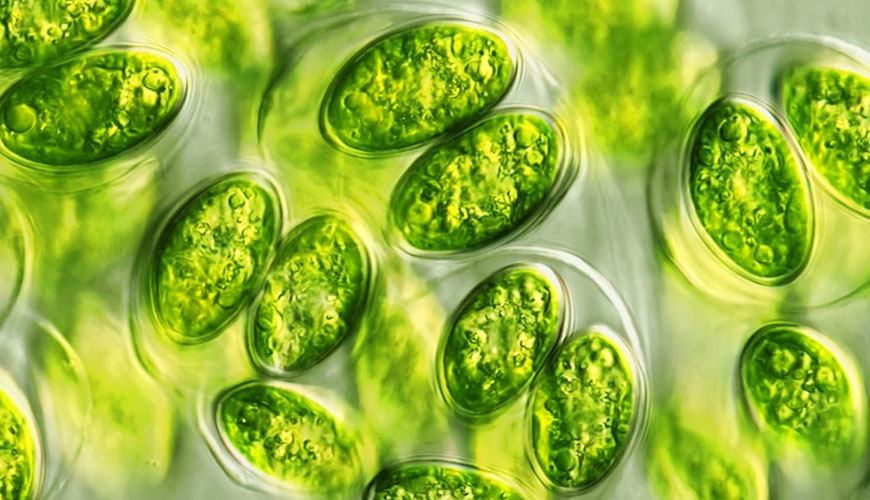
Single species of algae strains are cultured for several generations in a defined medium containing various concentrations of the test sample prepared by mixing appropriate amounts of growth medium, the test sample, and an inoculum of exponentially growing algae cells. Test batches are incubated for a period of 24 ± 72) hours during which the cell density in each test solution is measured at least every 2 hours. Inhibition is measured as a reduction in specific growth rate relative to control cultures grown under the same conditions.
All equipment that comes into contact with the test environment must be made of glass or other chemically inert material. The temperature-controlled cabinet or room with white fluorescent lights provides continuous, uniform illumination that meets the specified lighting requirements for the test.
To measure algal cell density, the device is preferably used with a particle counter capable of counting particles from 2,5 µm to 25 µm (spherical diameters), or a microscope and a counting chamber.
Alternatively, algal densities can be determined by an indirect procedure using, for example, in vivo fluorescence enhanced with a fluorimeter (for example, in vitro fluorescence or DCMU5), when sensitive enough and shown to correlate well enough. cell density. The apparatus used should be able to measure cell densities as low as 104 cells/ml and distinguish between algae growth and irritating effects, such as the presence of particulate matter and the color of the sample. Spectrophotometers can be sensitive enough to measure 10 cells/ml, providing a sufficient path length (up to 104 cm). However, this technique is particularly susceptible to interference from suspended material and colored matter at low cell densities.
Among the services provided by our organization within the framework of material testing services, there are also ISO 8692 standard tests. Do not hesitate to contact our laboratory EUROLAB for your testing and certification requests.
To get an appointment, to get more detailed information or to request an evaluation, you can ask us to fill in our form and reach you.