

EUROLAB laboratory provides testing and compliance services within the scope of EN 12791 standard. The EN 12791 standard specifies a test method that simulates practical conditions to determine whether a product for surgical handrub and handwashing reduces resident release and eventually presents transient microbial flora on the hands when used for the treatment of volunteers' clean hands.
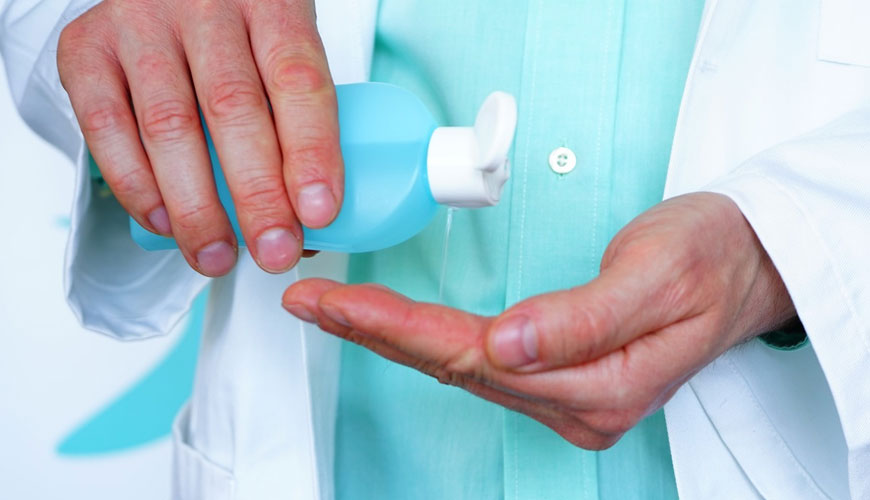
This European Standard applies to surgical handrub or handwash products for use in areas and situations where disinfection is medically indicated. These indications occur in patient care, such as:
It may also include services that provide products directly for the patient, such as laundries and kitchens. EN 12791 details how various tests relate to each other and use recommendations. This method corresponds to a stage 2, step 2 test.
Antiseptic treatment of the team's hands prior to surgical interventions in medicine is a standard procedure used worldwide to reduce the risk of infection. There are essentially two different types of antiseptics: alcohol-based hand aprons and antimicrobial liquid detergents.
Many standards have been developed to determine the antimicrobial activity of such preparations. The European standard EN 12791 published in 12971 is one of them. This standard provides a test method for antimicrobial efficacy that allows to reduce resident hand flora.
This test method evaluates whether a product used in surgical hand disinfection reduces the release of clean hand flora and is applied for products used in surgical hand disinfection by rubbing, as well as in hygienic hand washing.
During testing, hands are washed to remove transient flora and foreign matter and then to determine bacterial count prior to disinfection treatment. The test product is then applied and counts are made immediately and three hours after disinfection.
In this way, the ratio of the values obtained after three hours and corresponding to the reduction factor before and after the disinfection process is obtained. The results obtained with the reference method of surgical hand disinfection applied to the same people using prospenol should be compared with the results at a rate of -1-60%.
In short, this European standard applies to surgical handrub or handwash products used in medically disinfected areas and situations. These indications are often seen in hospitals, healthcare facilities, dentists and nursing home clinics.
To get an appointment, to get more detailed information or to request an evaluation, you can ask us to fill in our form and reach you.