

The thermal conductivity coefficient is a material parameter that changes depending on the physical properties of the material, water content, temperature and pressure on the material. In general, a material with a high thermal conductivity coefficient is a good heat conductor. A material with low is known as a good heat insulator. Therefore, this parameter has a pronounced effect both on the operating conditions in deep mines and on the thermal energy storage capacity of underground openings. On the other hand, thermal conductivity coefficient is taken into account in studies related to geothermal energy production and radioactive waste disposal. According to the experimental results obtained from various rock types such as basalt, marble and granite, the thermal conductivity of the rock depends on a number of factors such as temperature, axial stress, environmental pressure and structural properties. The thermal conductivity of the briefly mentioned rocks increases with increasing axial stress and increasing ambient pressure, but decreases with increasing temperature.
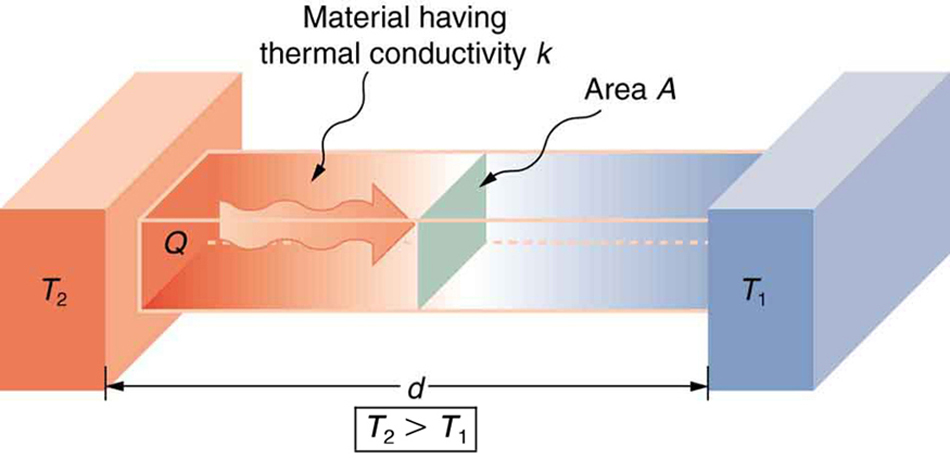
Thermal conductivity is the ability of a material to conduct or transfer heat. The inverse of this value is known as thermal resistivity. Materials with high thermal conductivity are used in coolers, and materials with low this value are used as heat insulators. According to Fourier's law of thermal conduction, the rate at which heat is transferred through a material is proportional to the negative of the temperature gradient. It is also proportional to the area through which the heat flows.
Various methods are used to determine the thermal conductivity of materials. These methods are generally of two groups: transient techniques and steady state techniques.
In transient techniques, measurements are taken during the heating process. Measurements can be taken relatively quickly. However, it is difficult to analyze the data obtained from the measurements mathematically. A few of these techniques are the temporary plane welding method, the temporary line welding method, and the laser flash method.
Steady-state techniques involve measurements where the temperature of the material does not change over a period of time. Since the temperature is constant, its analysis is relatively simple. However, performing tests usually requires a very well-designed setup. A few of these techniques are the stick method (Searle) and the disc (Lee) method.
Our organization also provides thermal conductivity coefficient analysis services with its trained and expert staff and advanced technological equipment, among the numerous test, measurement, analysis and evaluation studies it provides for businesses in various sectors.
To get an appointment, to get more detailed information or to request an evaluation, you can ask us to fill in our form and reach you.